Supported Formats
Generic Repository
Early Access
The Generic format and upstreams are in Early Access. Contact us to enable it for your organization
Cloudsmith provides public & private repositories for Generic files
Cloudsmith supports Generic files, a flexible format for managing any file or binary that relies on specific file paths rather than semantic versioning.
HTML-based upstreams
Generic upstreams work with simple HTML-based sources. The upstream must consist of simple, unstyled HTML pages with no JavaScript. Each page should contain only links to package files or subdirectories. Examples include Gradle distributions, Apache releases, and Node distributions.
Contextual Documentation
The examples in this document are generic. Cloudsmith provides contextual setup instructions within each repository, complete with copy and paste snippets (with your namespace/repo pre-configured).
In the following examples:
| Identifier | Description |
|---|---|
| OWNER | Your Cloudsmith account name or organization name (namespace) |
| REPOSITORY | Your Cloudsmith Repository name (also called "slug") |
| TOKEN | Your Cloudsmith Entitlement Token (see Entitlements for more details) |
| USERNAME | Your Cloudsmith username |
| PASSWORD | Your Cloudsmith password |
| API-KEY | Your Cloudsmith API Key |
| PATH_TO_FILE | The local path to the file you want to upload (e.g., ~/downloads/file.tar.gz) |
| FILEPATH | The repository path where the file will be stored (e.g., path/to/file.tar.gz) |
| UPSTREAM_PREFIX | Optional upstream prefix (e.g., node_distributions/) for files cached from upstreams |
Why Generic Format?
The Generic format is designed for artifacts that rely on specific file paths rather than semantic versions. Key benefits include:
- Path-Based Identification: Uses the filepath as the unique identifier, enabling exact replication of upstream directory structures
- Upstream Proxying and Caching: Proxy and cache files from simple HTML-based upstream sources
- Supply Chain Management: Bring custom scripts, installers, and binaries into your managed supply chain
- Consistent URLs: Internal URLs remain consistent with upstream sources
Generic vs Raw Format
The Generic format is optimized for path-based file distribution and upstream proxying. It relies strictly on the filepath as the unique identifier and does not support:
- Package naming (separate from filepath)
- Package versioning (semantic versions)
- End User License Agreements (EULA)
If you need package naming, semantic versioning, or EULA support, use the Raw format instead. The Raw format provides traditional package management features including distinct package names, version tracking, and license acceptance workflows.
File-Based Storage
Generic packages are treated as files and binaries. Unlike native package formats (Python, npm, Maven), Generic packages do not have metadata, version information, or vulnerability scanning capabilities. They are stored and served as-is without package-specific processing.
Upload a File
Upload via the Cloudsmith CLI
For full details of how to install and setup the Cloudsmith CLI, see Command Line Interface
The command to upload via the Cloudsmith CLI is:
cloudsmith push generic OWNER/REPOSITORY PATH_TO_FILE --filepath FILEPATHExample:
cloudsmith push generic your-account/your-repo ~/downloads/file.tar.gz --filepath distributions/latest/file.tar.gzFilepath parameter
The
--filepathparameter specifies where the file will be stored in the repository structure. This path becomes the unique identifier for the package and determines its download URL.
Upload via Cloudsmith web app
Please see upload a package for details of how to upload via the Cloudsmith web app.
Download a Package
Download via Cloudsmith web app
Public Repositories
When logged into Cloudsmith via a Web Browser, use the Download button located within the traffic light button dropdown on the package details page to download a generic package.
Private Repositories
For downloading from a private repository via the Cloudsmith web app, use the Use Package button to download a generic package using the default Entitlement Token for the repository. Use the dropdown arrow within the pop-up window to select a different authentication method.
Download via Command Line
To download a Generic package, fetch uploaded files using a well-crafted URL. The package URL format is based on the filepath used when uploading.
Public Repositories
https://generic.cloudsmith.io/public/OWNER/REPOSITORY/FILEPATHFor files cached from an upstream with a prefix:
https://generic.cloudsmith.io/public/OWNER/REPOSITORY/UPSTREAM_PREFIX/FILEPATHExample curl commands to download a generic package from a public repository:
curl -sLf -O 'https://generic.cloudsmith.io/public/OWNER/REPOSITORY/path/to/file.tar.gz'With upstream prefix:
curl -sLf -O 'https://generic.cloudsmith.io/public/OWNER/REPOSITORY/node_distributions/latest/node-v4.9.1.tar.gz'Private Repositories
Private Repositories
Private Cloudsmith repositories require authentication. You can choose between Entitlement Token Authentication or HTTP Basic Authentication. The setup method will differ depending on what authentication type you choose to use.
Secrets management
Entitlement Tokens, User Credentials, and API-Keys should be treated as secrets. You should ensure that you do not commit them in configurations files along with source code, or expose them in any logs.
Using Entitlement Token authentication:
curl -sLf -O 'https://generic.cloudsmith.io/TOKEN/OWNER/REPOSITORY/FILEPATH'With upstream prefix:
curl -sLf -O 'https://generic.cloudsmith.io/TOKEN/OWNER/REPOSITORY/UPSTREAM_PREFIX/FILEPATH'Using HTTP Basic authentication:
curl -sLf -u "USERNAME:PASSWORD" -O 'https://generic.cloudsmith.io/basic/OWNER/REPOSITORY/FILEPATH'With upstream prefix:
curl -sLf -u "USERNAME:PASSWORD" -O 'https://generic.cloudsmith.io/basic/OWNER/REPOSITORY/UPSTREAM_PREFIX/FILEPATH'HTML Indexes
Cloudsmith supports serving Apache-style HTML formatted indexes of generic package files in the repository.
Disabled by Default
HTML index generation is disabled by default. Enable it in Repository Settings under the Generic section.
When HTML index is disabled, the repository only supports direct file downloads. Requests for specific files will still proxy and cache from configured upstreams (if the file exists on the upstream) or serve cached files from the repository.
When HTML index is enabled, requests to directory paths (without specifying a file) will return an HTML view showing the index of available files and subdirectories.
When enabled, the HTML index is available at:
Public Repositories
https://generic.cloudsmith.io/public/OWNER/REPOSITORY/Private Repositories
https://generic.cloudsmith.io/TOKEN/OWNER/REPOSITORY/https://generic.cloudsmith.io/basic/OWNER/REPOSITORY/Browser Access
To view the HTML index in a browser for private repositories, use
TOKENas the username and your entitlement token as the password when prompted for authentication.
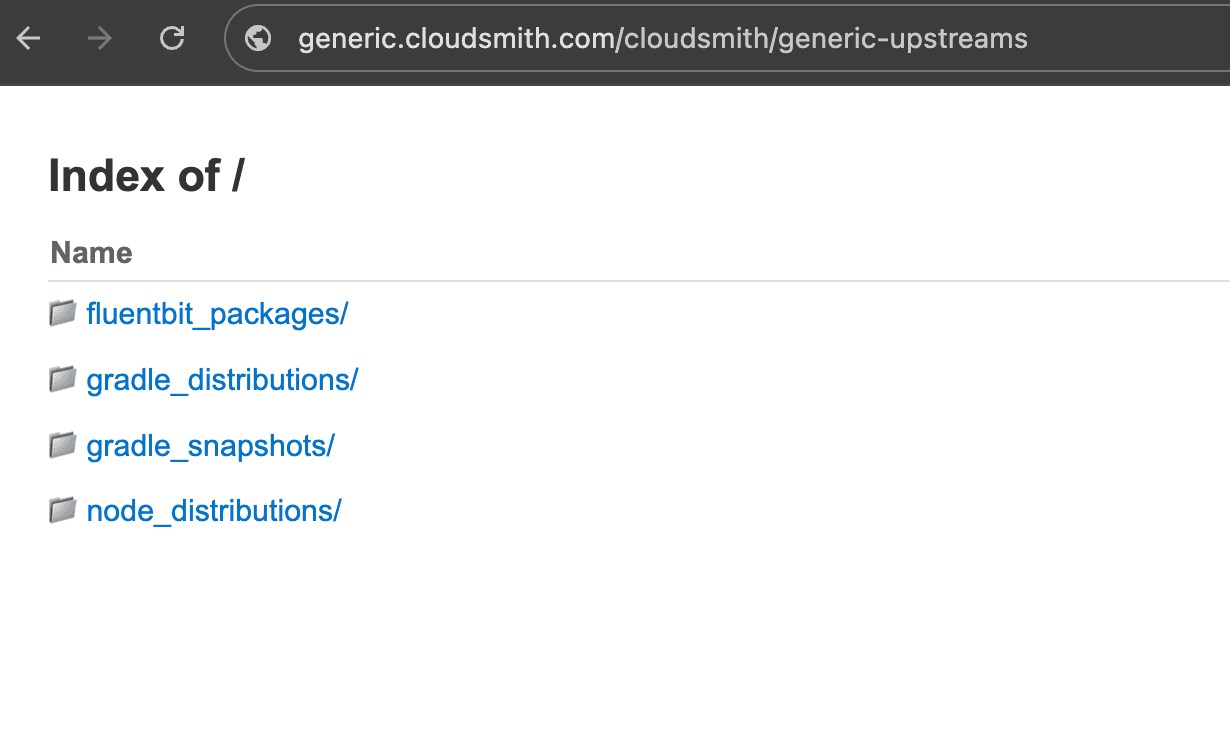
Upstream Proxying / Caching
SupportedThe Generic format supports upstream proxying and caching for simple HTML-based sources and select non-HTML sources. When a file is requested, Cloudsmith checks for a local copy. If missing, it fetches the file from the upstream, caches it as a first-class local package, and serves it.
Supported Upstream Sources
The following upstream sources are explicitly supported and work out of the box:
- Gradle - Gradle distributions
- Node - Node.js distributions
- Hashicorp - Hashicorp releases
- Fluentbit - Fluentbit distributions
- HTML-based sources - Simple, unstyled HTML pages with no JavaScript, where each page contains only links to files or subdirectories (e.g., Apache releases, Project Gutenberg)
Generic format accepts any files or binaries, not just traditional software packages.
Enterprise Repository Support
Enterprise repository managers like Artifactory and Sonatype Nexus require additional configuration and will not work out of the box. These sources also have practical size limits—repositories with millions of packages may not be processable. Contact support to discuss setup for these upstream sources.
Configure an Upstream
To configure an upstream for your Generic repository, browse to your repository overview page and click the Upstreams tab. Then, click + Add Upstream Proxy and choose the Generic format upstream.
In the upstream creation menu, define a name for your upstream and enter the upstream URL. Optionally specify an Upstream Prefix to prevent file collisions when using multiple upstreams. The prefix becomes part of the file's permanent path in the repository, ensuring files from different upstreams never collide even with identical filenames.
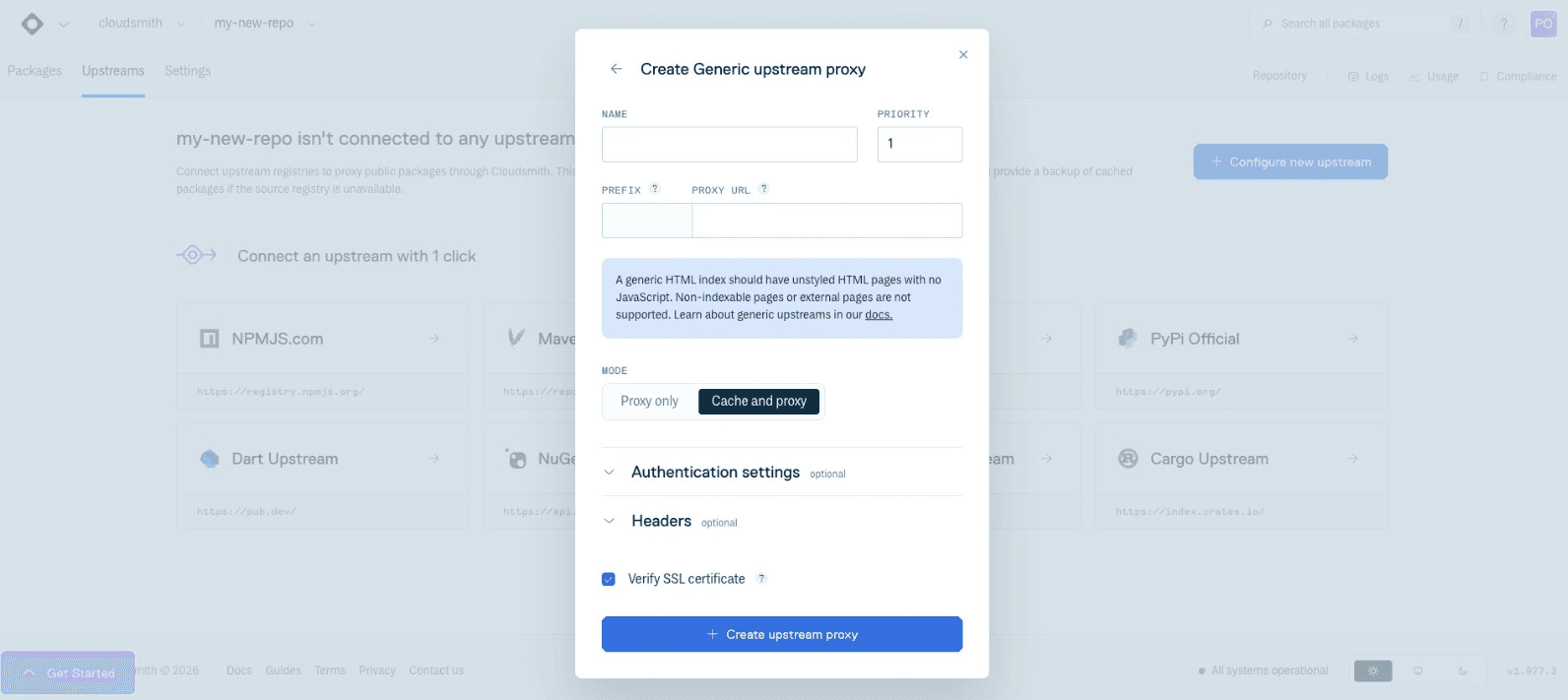
Please see our Upstream Proxying documentation for further instructions on configuring upstreams.
Upstream Priority
Upstream priority behaves differently for Generic repositories due to the nature of upstream prefixes. All upstreams within a prefix are given a priority of 1. Changing the priority setting does not impact package blending, as each upstream is uniquely namespaced within its own prefix.
Local packages (directly uploaded to the repository) always take precedence over upstream packages. When viewing the HTML index, cached packages display with a different icon than packages that will be proxied on demand.
Key Signing Support
GPGPlease see Package Signing for information about key support by package format.
Troubleshooting
Please see the Troubleshooting page for further help and information.